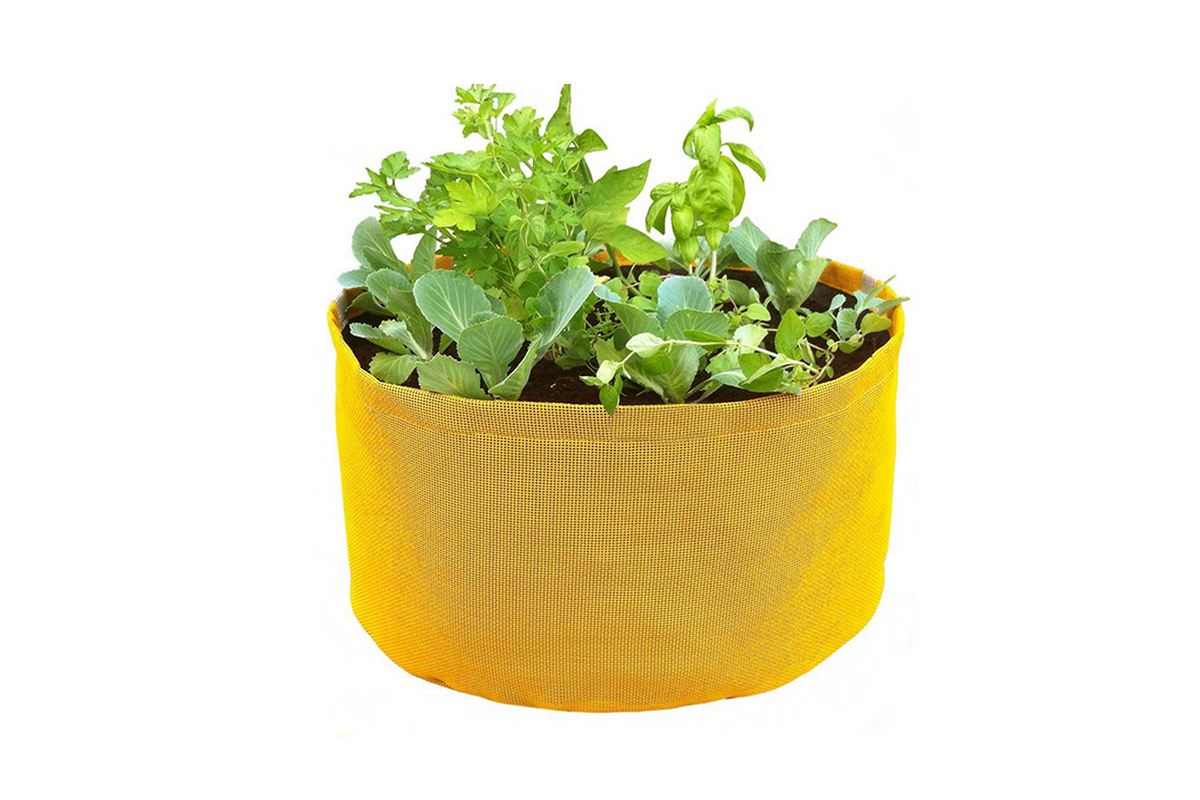
Custom fabric garden bags manufacturing factory
In the field of gardening, fabric garden bags play a convenient and flexible role in planting. Mastering the correct methods of filling soil and planting is crucial for the growth of plants in them.
I. Soil Selection and Fertilizer Matching
Soil Type
Selecting the appropriate soil for fabric garden bags is the foundation. Loose, fertile, and well-drained soil is preferable. General gardening potting soil is a common choice, which contains components such as leaf mold, peat moss, and perlite, possessing both water and nutrient retention as well as air permeability.
For special plants like acid-loving plants such as rhododendrons and blueberries, the soil pH needs to be adjusted. Sulfur powder or pine needle soil can be added to the ordinary potting soil to make it acidic.
Fertilizer Selection
Before filling the soil to fabric garden bags, fertilizers should be added according to the needs of the plants. Organic fertilizers can improve the soil structure and release nutrients slowly, providing long-term nutrition for the plants.
Slow-release fertilizers are also a good option. They release nutrients over time to meet the needs of different growth stages of the plants. Flowering plants mostly need fertilizers rich in phosphorus and potassium to promote flower bud differentiation and flowering, while vegetable plants require balanced nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizers to ensure growth and fruit development.
II. Filling Method and Key Points
Correctly Filling the Soil
Pour the selected soil slowly into the fabric garden bags. During the filling process, it is necessary to distribute the soil evenly. Small shovels or spoons can be used to assist, ensuring that every corner is filled. For larger fabric garden bags, a layer of coarse-grained materials such as ceramsite or gravel about 5 - 10 centimeters thick can be laid at the bottom to enhance drainage and prevent waterlogging and root rot at the bottom.
Controlling the Soil Thickness and Compaction Degree
The thickness of the soil depends on the plant species and the size of the fabric garden bags. For small flower plants, the soil thickness is about 15 - 20 centimeters. For vegetable plants or those with more developed roots, it can be increased to 20 - 30 centimeters.
After filling the soil to fabric garden bags, keep it moderately loose. Gently pat the soil surface to make it flat. Do not over-compact to avoid affecting the soil structure and air permeability.
III. Planting Spacing and Depth
Planting Spacing
The spacing between different plants varies. For flowers like petunias and pansies, the spacing is about 10 - 15 centimeters, which is beneficial for the expansion of branches and leaves and the formation of a beautiful flower cluster.
The spacing of vegetable plants depends on the variety and growth habit. For example, tomatoes are spaced 30 - 50 centimeters, and leafy vegetable plants like lettuce are 15 - 20 centimeters. Reasonable spacing ensures the growth space and nutrient utilization of the plants.
Planting Depth
The planting depth of seeds is 1 - 2 times their diameter. Fine grass flower seeds are scattered on the soil surface and covered with a thin layer of soil. Larger vegetable seeds such as beans and corn are about 3 - 5 centimeters. When transplanting seedlings, the complete root system should be placed in the planting hole, filled with soil and ensure full contact between the soil and the root system. The depth should be moderate, too deep or too shallow is not conducive to growth.
IV. Planting Skills and Precautions
Avoiding Damaging the Root System
Be careful during planting to avoid damaging the root system. When transplanting seedlings, use a small shovel to dig a hole and keep the root system intact and stretched. When filling the soil, gently cover the soil to avoid impacting the root system.
Watering Method
Water thoroughly in time after planting to make the soil and root system closely combined. In the subsequent maintenance, water reasonably according to the plant's needs and weather conditions. Keep the soil moist but not overly wet. You can use your finger to probe the soil to judge the humidity.
Fertilization Points
Apply fertilizers timely during growth and follow the principle of "thin fertilization and frequent application". Apply thin liquid fertilizers or water-soluble fertilizers every 1 - 2 weeks. Observe the growth status and adjust and supplement nutrients in time when there is a lack of fertilizer.
Other Precautions
When selecting plant varieties, consider whether their adaptability and growth habits are suitable. Regularly check the fabric garden bags for any damage, soil loss, and other issues. Pay attention to preventing and controlling pests and diseases and keep the surrounding clean and hygienic.
In conclusion, the correct methods of filling soil and planting are the key to the healthy growth of plants in fabric garden bags. Reasonable soil selection and fertilization, mastering the filling skills, paying attention to spacing and depth, and scientific management can make use of their advantages to create a beautiful small garden. Whether on the balcony, in the courtyard, or in other spaces, fabric garden bags provide a convenient way to realize the green dream.

 en
en Español
Español